Microwave-assisted Self-healable bio-vitrimer/rGO framework for Anti-corrosion application
Singh, P. et. al. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16, 40, 54693–54705, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c13361
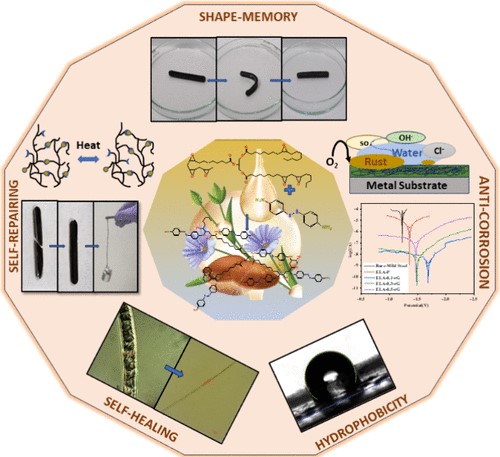
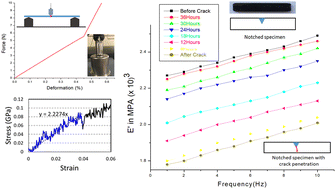
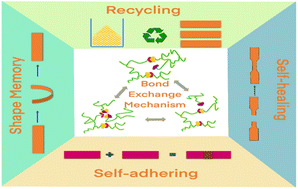
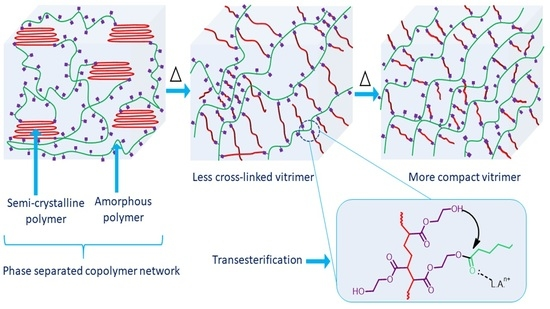
A versatile and robust end-group derivatization approach Microwave-stimulated smart self-healable polymeric coatings with significant protective technology against corrosion have been developed in this work. Herein, a generous approach is strategized to generate linseed oil-derived epoxy composites embedded with reduced graphene oxide (rGO) as a nanofiller in the shielding network. The composite showed excellent self-healing and shape memory properties when irradiated with microwaves due to the dynamic reversible nature of the disulfide covalent bond exchange mechanism. The network also has improved thermomechanical properties and thermal stability, with a storage modulus of 20.8 GPa and a low activation energy of 79 kJ/mol, indicating a fast disulfide dynamic exchange reaction. The amine functionality in the composite contributes to excellent corrosion protection, with 99.9% protection efficiency, as validated via a Tafel plot. The composite also showed excellent hydrophobicity, with a 131° contact angle. This study provides insights into the engineering and application of smart materials as anticorrosive coatings. Copyright © 2024 American Chemical Society.