Proximity Effects and Aggregation of Hamilton-Receptor Barbiturate Host-Guest Complexes Probed by Cross-Metathesis and ESI MS Analysis
Li, C. et. al., Chem. Europ. J., 2025, 31, 8,e202403939, https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202403939
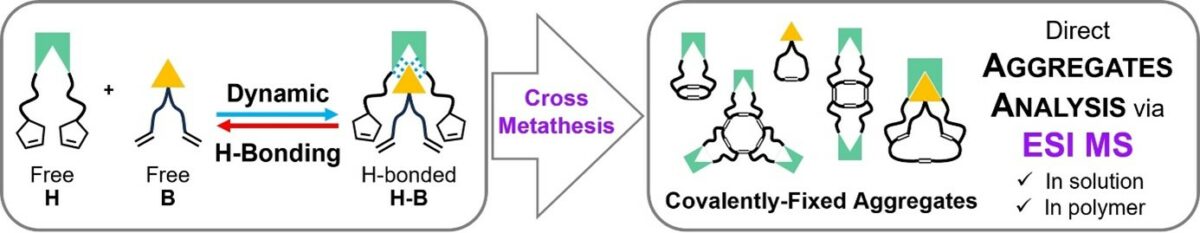
The molecular environment around supramolecular bonding systems significantly affects their stability and the assembly of host–guest complexes, most prominent for hydrogen bonds (H-bonds). We here investigate the formation of higher order assemblies of hydrogen bonds, using the Hamilton receptor-barbiturate host–guest complexes as a model system. A novel Hamilton receptor (H) was equipped with cyclopentene moieties and used as a host to form host–guest complexes (H−B) with allobarbital (B), followed by covalent crosslinking. Higher-order aggregates (HH-dimer, HHH-trimer) were subsequently detected via an alkene cross-metathesis (CM) reaction to fix the assemblies covalently, followed by analysis via electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI MS). This two-step method, firstly via CM fixation followed by ESI MS, was extended to study the H−B model complex within a polyisobutylene (PIB) matrix, presenting a direct method to analyze the complex host–guest assembly in solvent-free (polymer) environments. © 2024 The Author(s). Chemistry – A European Journal published by Wiley-VCH GmbH. Open access